How to Write a Business Plan for a Mobile App


A well-structured business plan plays a vital role when seeking investments for your project. With its help, you can streamline all facets of your venture, bringing clarity to what might otherwise seem chaotic. Let’s delve into effective strategies for developing a plan that not only benefits you as an entrepreneur but also guides your team towards success!
Why Make A Mobile App Business Plan?
A business plan lays the foundation for any project, allowing you to:
- Develop detailed business strategies
- Objectively assess outcomes
- Calculate how to allocate available resources etc.
Moreover, this document aids in team management by ensuring:
- Clear understanding of goals for all team members
- Proper prioritization and KPI determination
- Building trust with investors and stakeholders
According to THIS survey, initiatives supported by a BP are twice as likely to succeed!
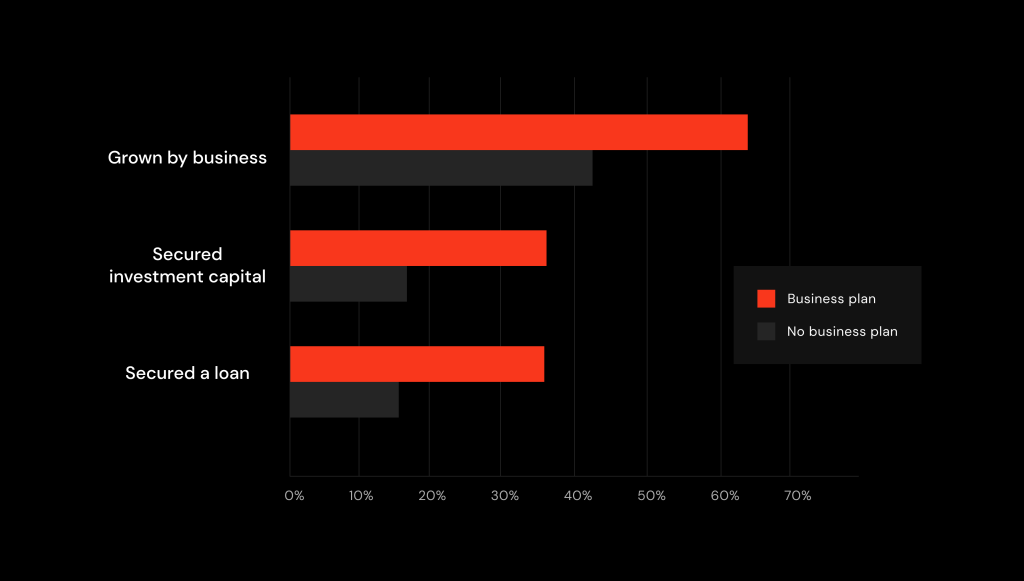
Usually, a typical business plan comprises different chapters like product description, audience analysis or financial Strategy. Generally, these sections span 20–40 pages, although the length may vary based on project size and objectives. When crafting a document, it is important to tailor it to the intended audience i.e. present information concisely to maintain reader engagement (particularly crucial when targeting investors who value their time!). Aim for brevity without compromising essential details! Let’s talk about all the essential steps in detail.
Steps To Create a Business Plan For Your Mobile App
First, we suggest focusing on fundamental guidelines to aid you in the process:
✓ Ensure your BP is reader-friendly. While the content can be intricate, the overall document should offer easy navigation and comprehension. Employ clear headings, subheadings, proper formatting, and ample white space. Each section should seamlessly transition into the next, with key points accentuated through graphs and visuals.
✓ Present realistic estimations to avoid deterring potential investors and jeopardizing the business’s viability in the long run. Although optimism is essential, forecasts should strike a balance by showcasing the startup’s promising future and the potential returns for investors. If projections appear bleak, it might be prudent to reconsider the venture’s direction.
✓ Seek assistance! It is not only acceptable but beneficial! Invite feedback from individuals, preferably those with experience, to review each section meticulously. External viewpoints ensure the coherence and effectiveness of the whole document.
Summary
It encapsulates the essence of the entire document. It should touch upon the current market landscape, target audience, project concept, business objectives, and financial forecasts. Essentially, this section addresses three fundamental questions:
- What is the venture about?
- What purpose does it serve?
- Who is the intended audience?
Craft your summary to stand alone as a compelling document. Given that many investors base their initial decisions on this section, its significance is paramount, particularly for fundraising efforts.
Your objective is to entice the reader with the idea’s potential without inundating them with extensive tables or abstract research. Ideally, the summary should not exceed 2-3 pages.
Company Overview
This section offers insight into your company. Structure your narrative around key elements:
- Mission: Briefly articulate the company’s main purpose. For instance, Google states, “Our mission is to organize the world’s information and make it equally accessible to everyone.”
- Vision: Outline the impact your company strives to achieve
- Corporate values
- History and past accomplishments (if applicable)
- Organizational structure (briefly!)
- Competitive advantages
Furnish comprehensive details about your team. How many members constitute the team and what are their superpowers? Give special attention to top management and key personnel within the company. Highlight their skills to demonstrate your venture not only offers an innovative idea but also boasts talented professionals. Delve into equity distribution intricacies. Does each partner hold an equal stake in the company? If not, elucidate on the property division structure. Potential investors will seek clarity on this aspect!

Product Description
Let’s delve into the core of your idea. Begin by elucidating the problem you aim to address:
- Who is impacted by the issue?
- How does it affect this demographic?
- Why is resolving this problem important?
While supporting your assertions with research and statistics is beneficial, refrain from inundating this section with excessive numerical data. If there is substantial information, consider placing some in the Appendix.
Subsequently, transition to presenting your solution. Detail a specific niche you plan to target (healthcare, logistics, education, social media etc.) and the platforms it will be built upon, such as iOS, Android, or cross-platform options. Outline the concept and core functionality in a well-structured technical specification. Here, you should describe the application’s features, components, use cases. While detailing these specifications, it’s unnecessary to delve into technical jargon since investors are not developers. Instead, prioritize elucidating the key functionalities and overall concept.
Audience Analysis
It’s crucial to evaluate the market landscape and substantiate how your product will carve out its niche in the competitive arena. In this segment, you describe the target demographic, significant trends, consumer behavior patterns. You can calculate these key metrics to prove your point:
- Cost per conversion (CPA)
- Total addressable market (TAM)
- Serviceable addressable market (SAM)
- Share of market (SOM) that is realistically attainable.
Creating a user portrait is a vital step. These are generalized representations of individuals who would express interest in your solution. Do not take any theories as a basis, engage in comprehensive REAL interviews! Segment the gathered information into various categories:
- Demographic details: age, gender, income, location
- Psychographic insights: aspirations, obstacles, driving factors, personality traits
- Professional background: current employment status, experience levels etc.
- Interests, preferences
- Needs: elucidate why these individuals require your product.
Competitor Analysis
Having briefly covered competition in the summary, it’s time to delve into this topic comprehensively. Conduct a proper evaluation of both your direct and indirect competitors, dissect their strategies, analyze pricing tactics. Following competitor analysis, redirect the focus to your product once again and describe the aspects where it outshines its rivals.
Marketing Strategy
In this segment, outline three crucial components. Firstly, specify the promotional channels you intend to utilize—these could encompass social networks and targeted ads. Next, detail your projected marketing expenditures. Finally, delineate the key performance indicators (KPIs) that will gauge the strategy’s effectiveness.
Financial Strategy
That’s the cornerstone of any business plan! Let’s outline the essential calculations needed here:
Revenue:
- Monetization strategy (like in-app purchases or freemium model; you can check all options in our article HERE);
- Monthly sales and revenue forecasts for the initial 12 months, along with annual projections for the subsequent 3–5 years;
Financial resources you have and financial resourses you need:
Of course, the cost of developing an app is influenced by numerous factors like quantity of screens, design intricacy, integration with third-party services, and more. Additionally, creating an application for various platforms increases both the cost and duration of development. Hence, it’s advisable to segment the total cost into sections:
- Key features development
- MVP creation
- Testing, QA and refinement
- Submission to app stores
- The Launch phase
In summary, the final version of this section should contain the following info:
- Funding requirements: specifying the investment needed + ROIs calculated;
- Utilization of funds: articulating the allocation of the investment;
- If possible, add cash flow statement: detailing the company’s financial liquidity.
Understanding all these terms and incorporating them during pitches can boost investor confidence in entrepreneurs who have a solid grasp of financial concepts!
Annex
This section is optional but ideal for including graphs,, legal notices, reports, images—essentially, any information that may not seamlessly fit within the main sections.
App business plan template
Our clients often ask us if there is a difference between creating a business plan for a mobile app compared to other types of software. Certainly, when it comes to mobile apps, websites, and other solutions, there are clear distinctions that set them apart. These variations encompass marketing strategies, ways of generating revenue, and the features they offer. Consequently, the business plans tailored for these different solutions will reflect these differences! Thus, the content within each document will be unique, however, the structure is usually strandard:
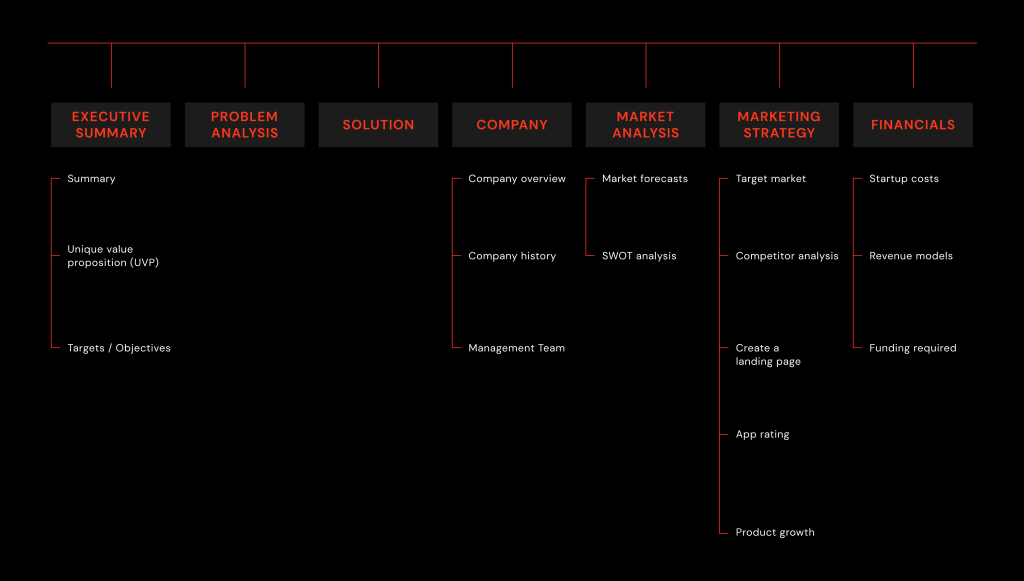
Conclusion
The most challenging aspect of developing a business plan for a mobile app idea often lies in crafting that initial page. Startups may be tempted to take a shortcut by seeking out and copying another company’s BP, assuming it will work just as well for them. However, this approach is flawed! Instead, it should be a reflection of your overarching objectives, mission, and belief in realizing your idea, presenting your company as a viable, compelling, promising, and financially appealing one!
FAQ
-
What is a business plan for a mobile app?
- No doubt that a mobile app business plan is a strategic document. Startups can’t base their concept on personal opinions or unproved theories as risks are too high. Each phase must be thoroughly calculated, backed by real numbers and surveys. Thus, such a business plan for app projects usually outlines main objectives, TA, promo approach. Such app business plan typically includes a description of main features and development roadmap. Overall, the business plan app development serves as a roadmap for the successful creation, launch, and growth of your future product.
-
What types of mobile app business plan are there?
-
When it comes to app development business plan options generally fall into three main types:
- traditional one, which outlines the overall strategy and financial projections;
- lean startup plan, focusing on key hypotheses and testing strategies quickly;
- one-page option, providing a concise overview of the app’s value proposition and key elements.
Each type of a business plan for mobile app caters to different situations, offering varying levels of detail and flexibility in planning. -
What are the Steps To Start a Mobile App Business?
- Identify open opportunities and perspective niches. Next, analyze groups of individuals who might require your solution to solve their particular problem. Develop a business plan for an app so you could show it to potential investors. Your business plan for app development should also outline your general strategy. Besides a business plan mobile app developers should create a prototype and test it with users for feedback. These results usually convince investors to make the final decision, as they are based on real market results, not just theories.
-
What should I mention in my business plan? The product is a mobile educational platform for learning languages by watching your favorite TV shows?
-
Start by introducing the app’s concept as an innovative platform that enhances language acquisition through watching shows with subtitles and interactive quizzes. Outline the target market, highlighting demographics such as language learners, enthusiasts of foreign media, and individuals seeking a fun language-learning experience. Detail how the app will differentiate itself by combining entertainment with education, making language learning engaging and effective.
Describe key features, including a vast library of shows in multiple languages, personalized quizzes, progress tracking, and social sharing capabilities. Discuss the technology stack required for video streaming, quiz generation, user accounts, and data analytics.
Explain the revenue model, which can include subscriptions, in-app purchases for premium content or features, and potential partnerships with content creators or language institutes.
Do not forget to address the marketing strategy, focusing on user acquisition through social media campaigns, influencer partnerships, and targeted advertising to reach language learners worldwide. Include a competitive analysis to identify similar language learning apps.
Provide financial projections, including development costs, operational expenses, and potential return on investment. Highlight scalability plans for future growth, such as expanding language offerings or integrating AI for personalized learning experiences.
Conclude with a summary emphasizing the app’s potential impact on language education, its market viability, and the team’s expertise in language learning and business management.



