Synthetic Data Generation Platform for Machine Learning Models
visynth.ai enables companies to generate high-quality synthetic images to train and validate computer vision models. Designed to address data scarcity, improve model performance, and streamline the workflow from dataset import to model training.
Main Goals
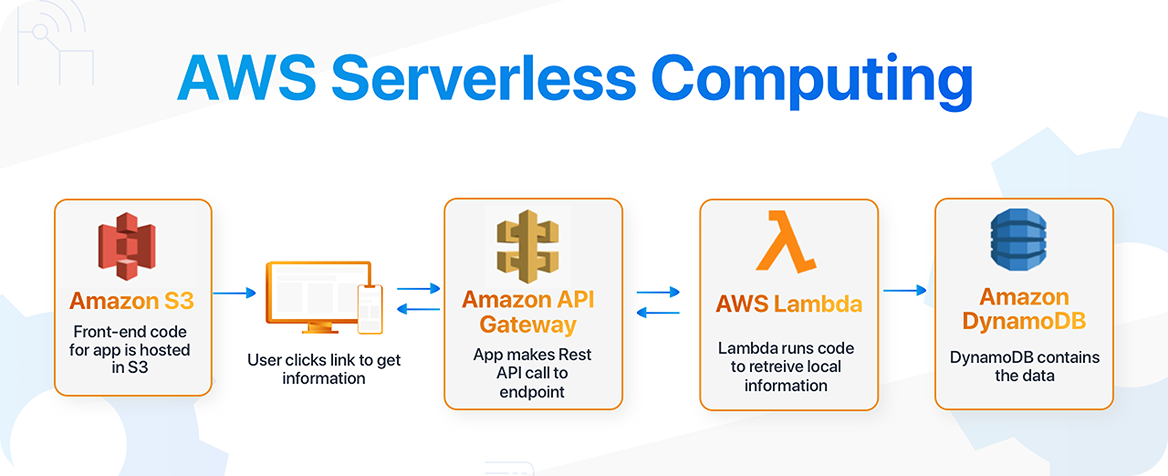
Our team helped build Visynth.ai from scratch, handling frontend dev, backend logic in Python, and serverless DevOps infrastructure on AWS.
Build a robust, serverless platform from scratch that can handle large datasets, AI model deployment, and data processing workflows.
Allow users to import, organize, and annotate datasets reliably, creating high-quality inputs for training and testing ML models.
Design and implement automated synthetic data generation with iterative refinement and human-in-the-loop feedback to improve model performance.
Challenge
Ensure the platform accurately analyzes incoming datasets and generates highly relevant and diverse synthetic images + maintains data quality and consistency.

Solution
We built a scalable serverless architecture using AWS Lambda, SageMaker, and Python, integrating custom frontend tools for annotation and feedback.
Let GenAI See What Other AI Vision Systems Miss
Go beyond scripted vision systems with adaptive GenAI that detects, learns, and acts; uncovering defects, drifts, and hidden issues no traditional model can.
Features
Allows users to manually label defects on images using polygons, curves, and bounding boxes. Ensures precise data preparation for training ML models and generating images.
Lets users define defect templates and configure their shape, size, and variation. This guides the generation of realistic synthetic images based on specific dataset requirements.

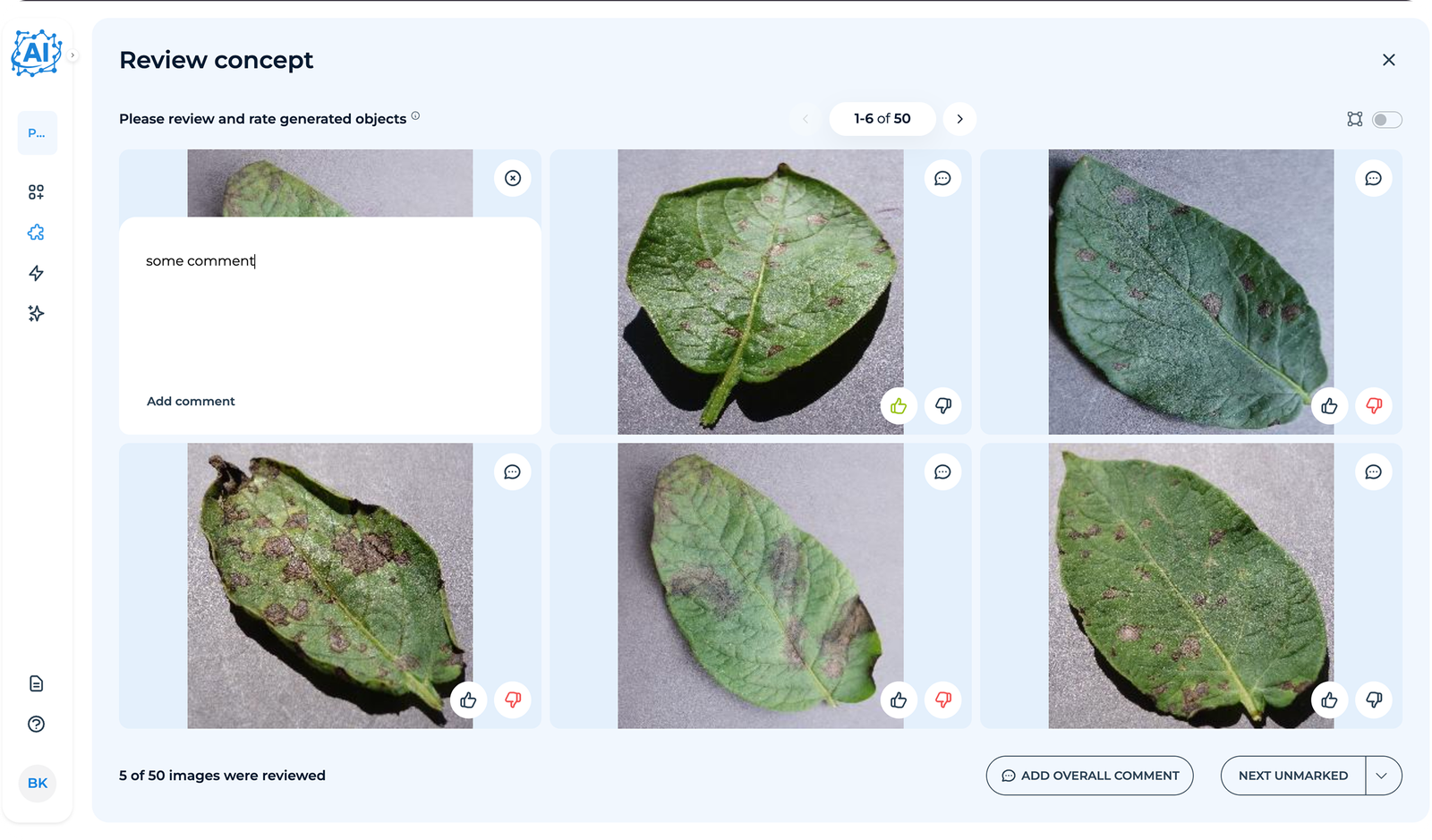
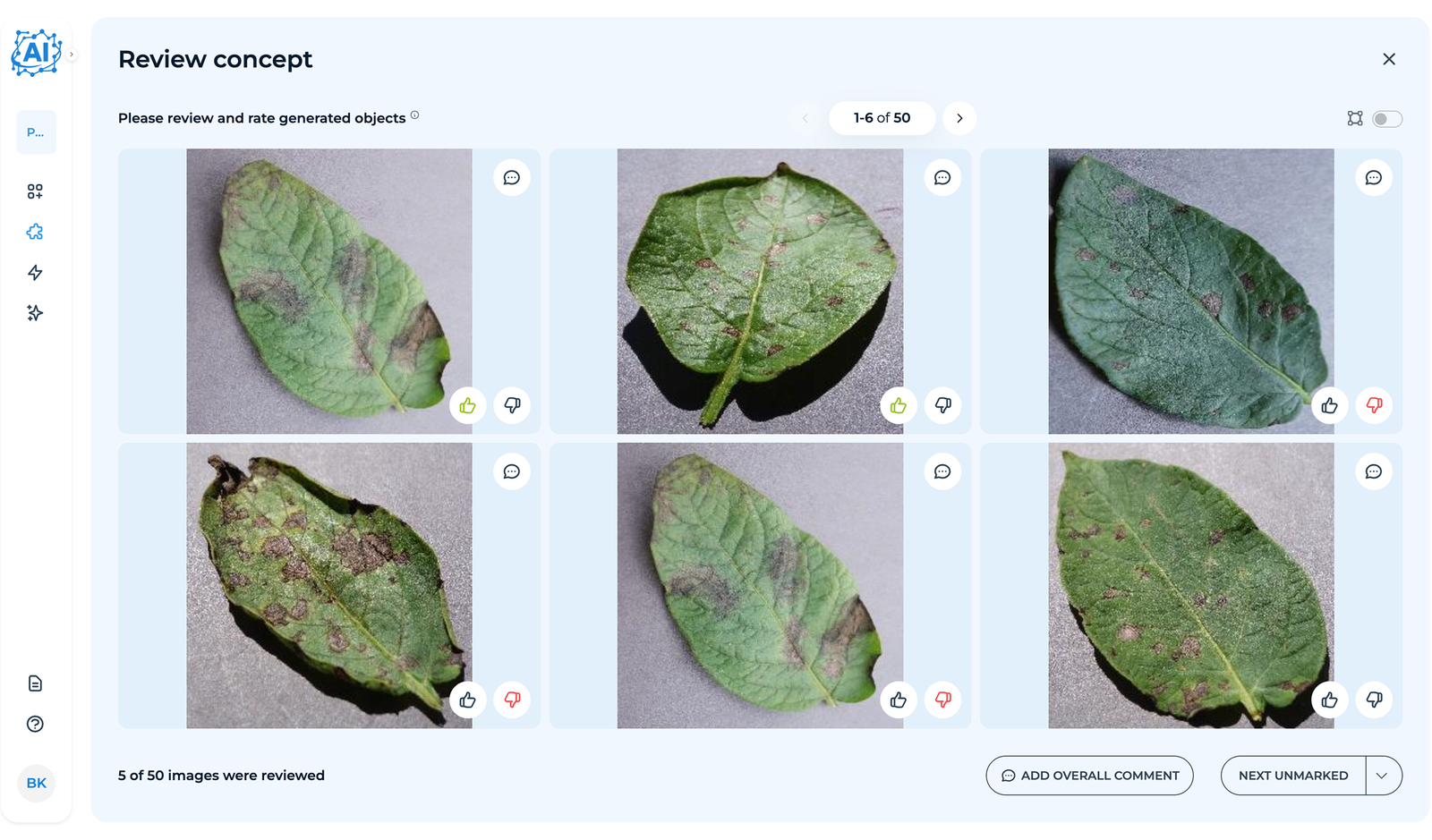
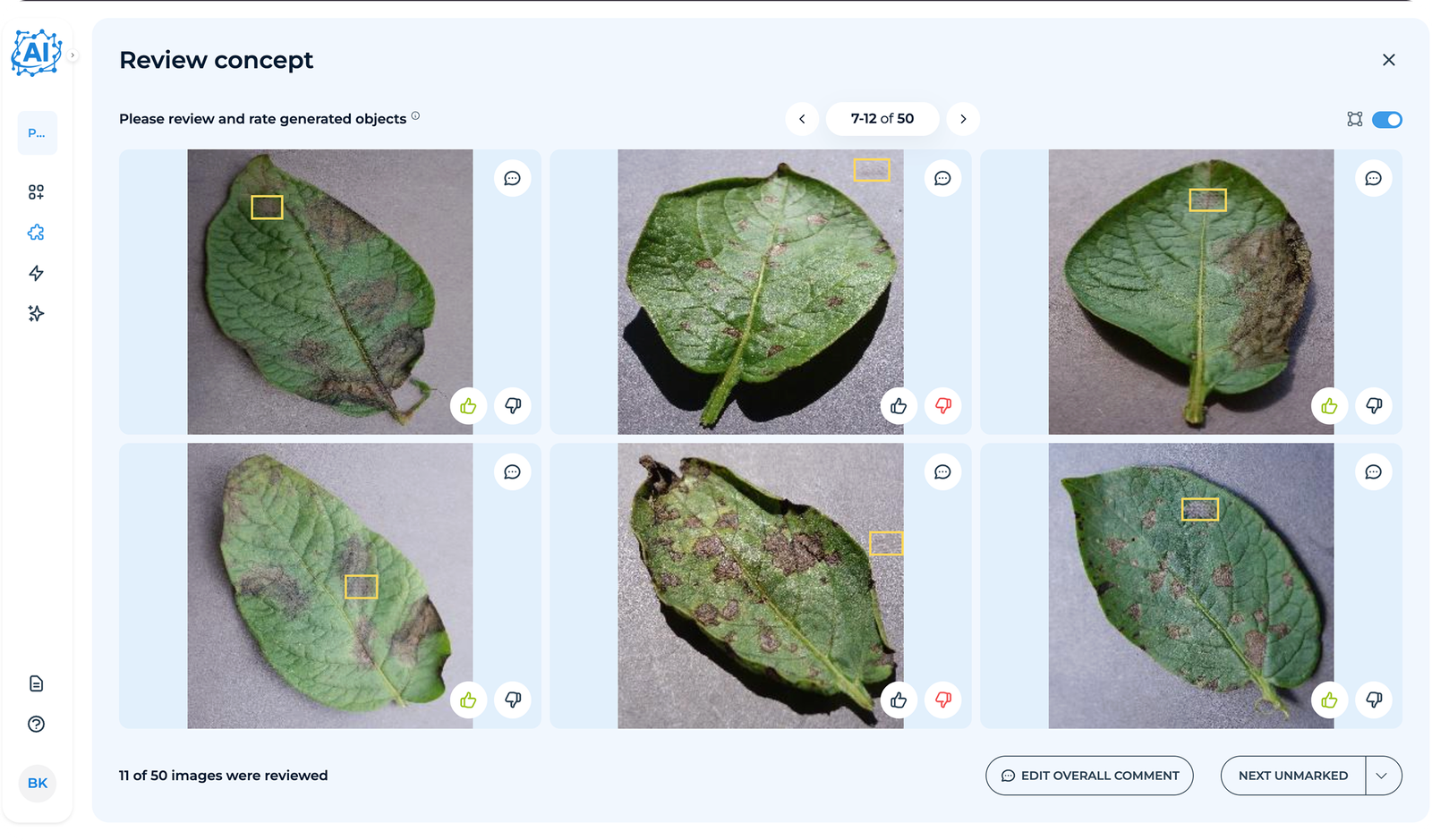
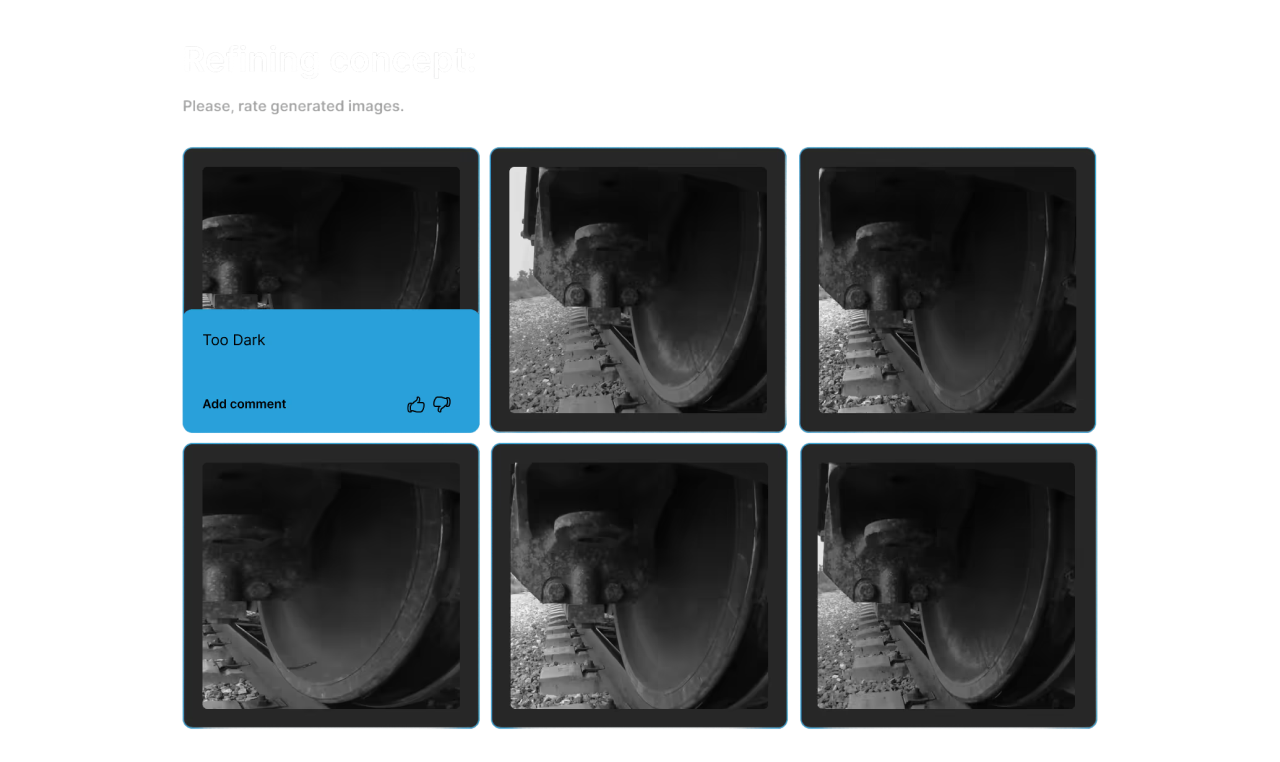
Users can review and provide feedback on generated images, after which the system iteratively regenerates them until the results meet user satisfaction.
Industries
From Initial Dataset
to Synthetic Data: Step by Step
After uploading images to AWS S3, users can select the corresponding dataset on the platform.
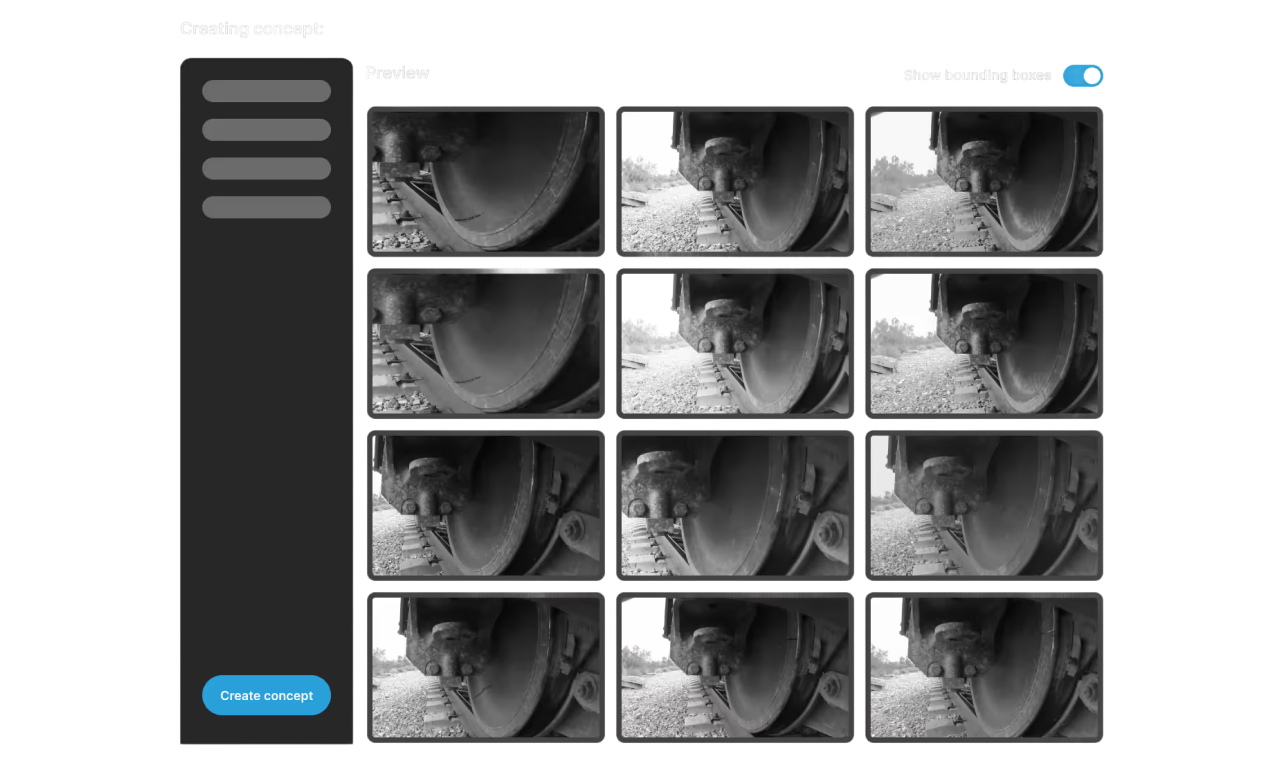
Users manually label defects or objects of interest on images using polygons, bounding boxes, or custom shapes. Black-and-white masks are generated for each class, which are later used for model training and data generation.
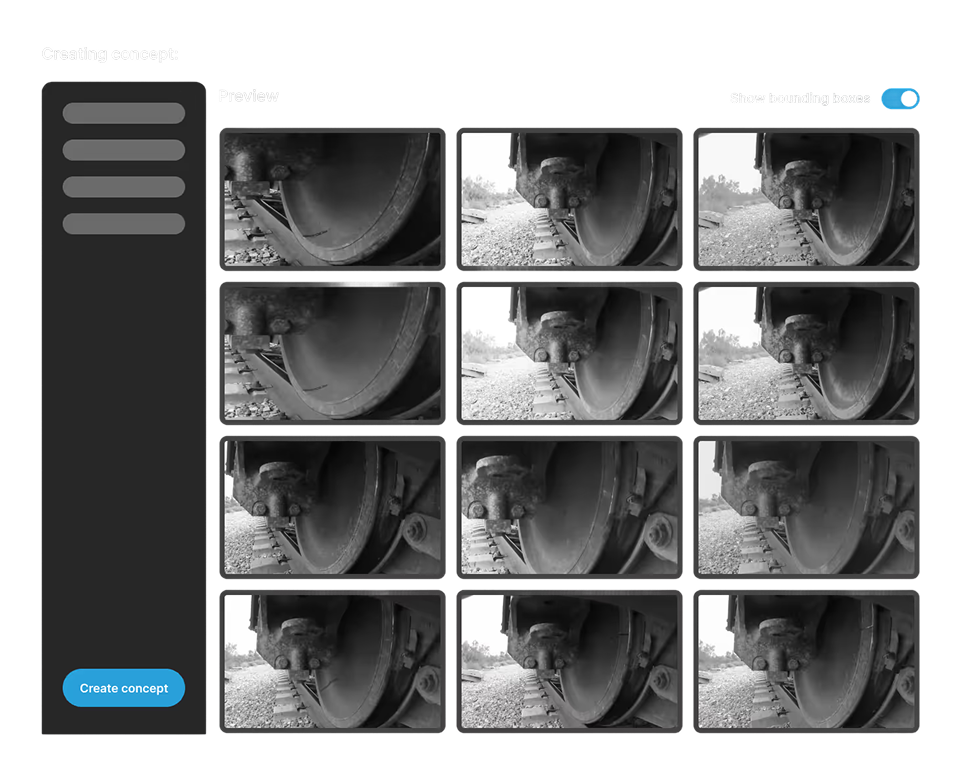
The platform iteratively generates images based on approved concepts. Users review a sample (e.g., 50 images), providing feedback on quality and accuracy.
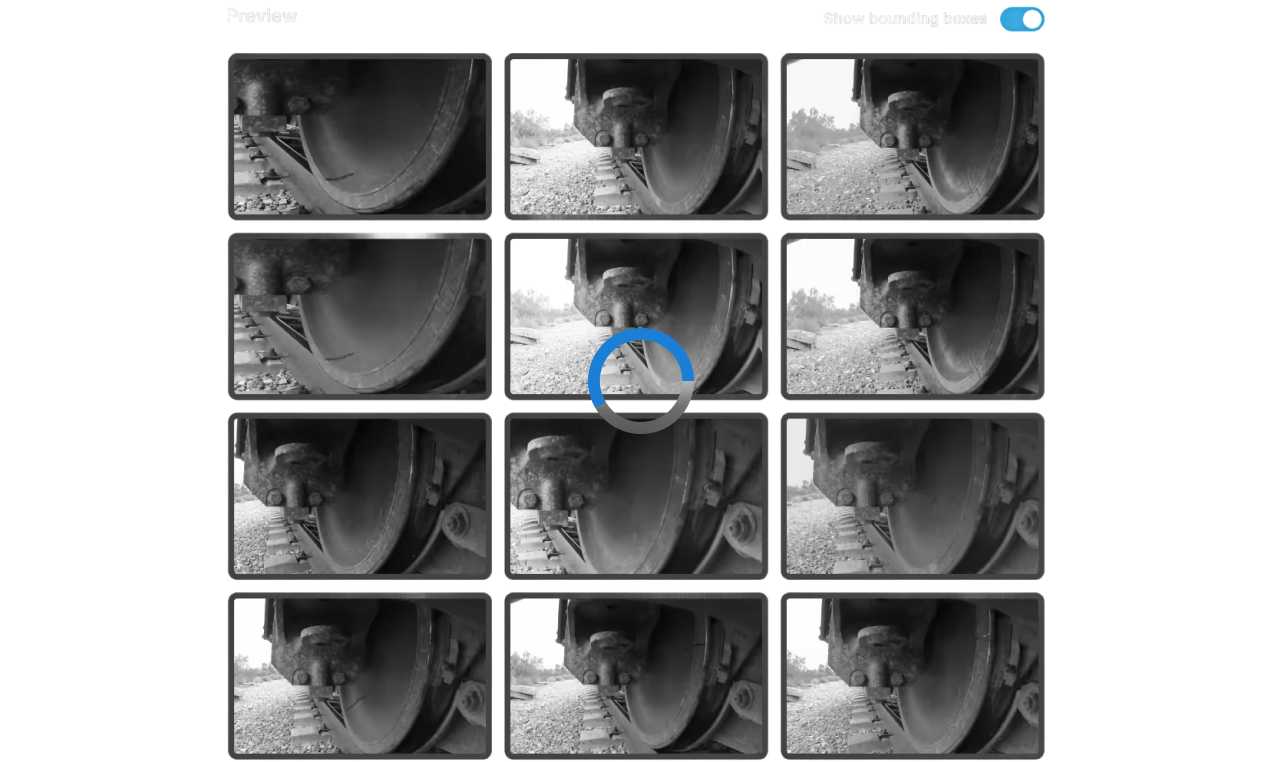
Feedback is processed automatically by the platform’s algorithms. Multiple versions of the concept are generated, each improving based on user input, until the client approves the results.
Once approved, the client generates a large batch of synthetic images (hundreds or thousands). These images are ready for export and can be used for training ML models.
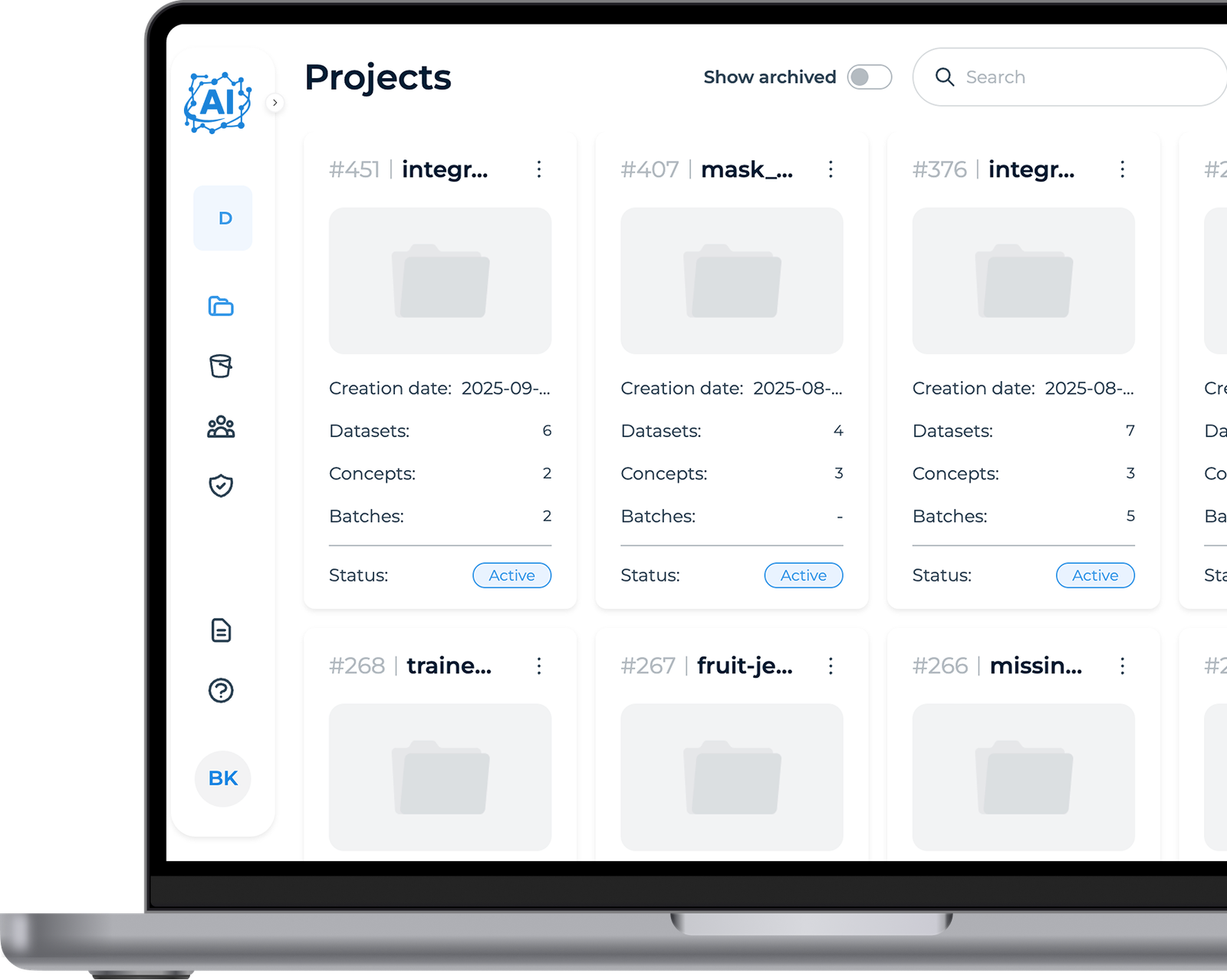
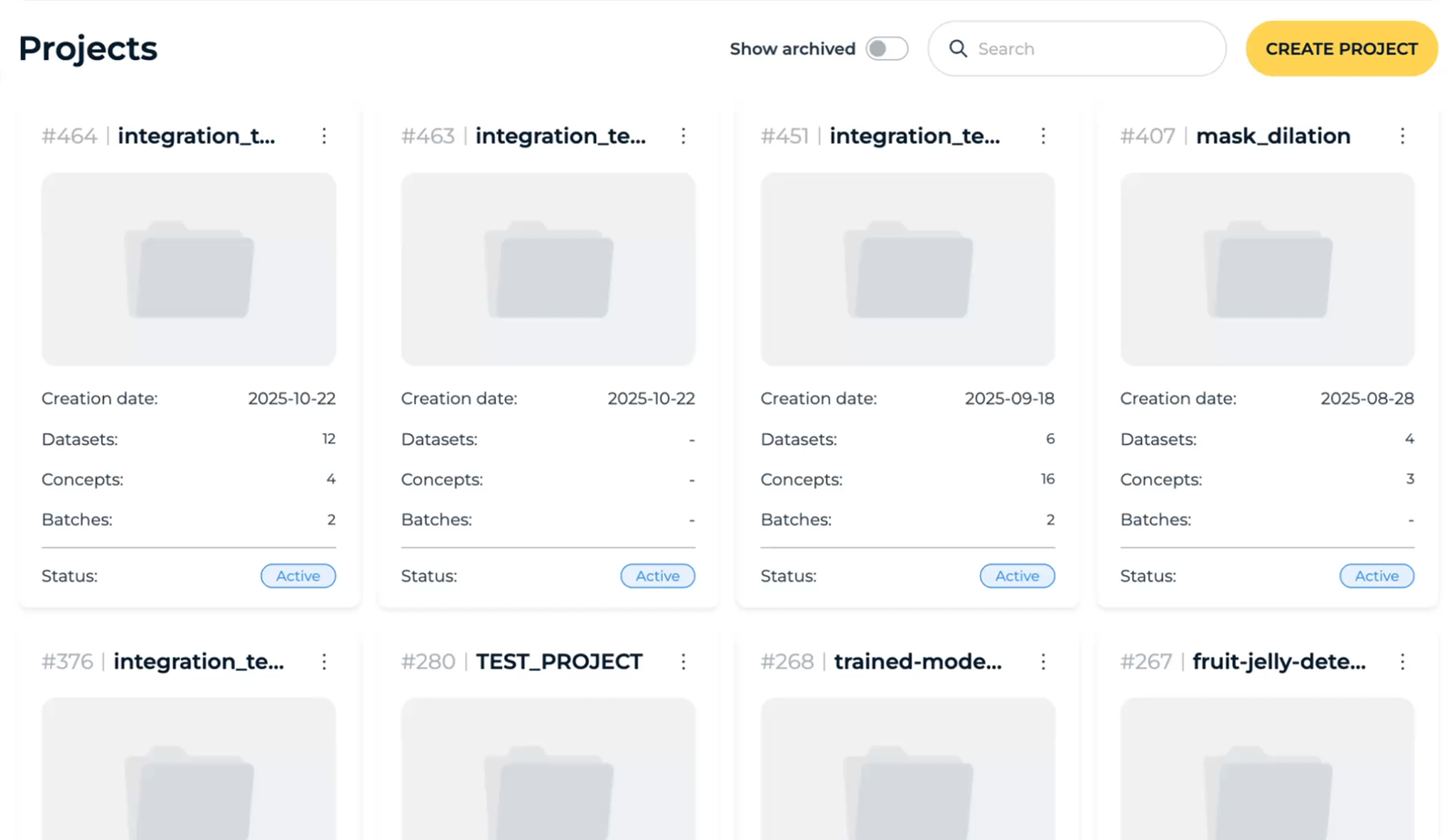
Projects
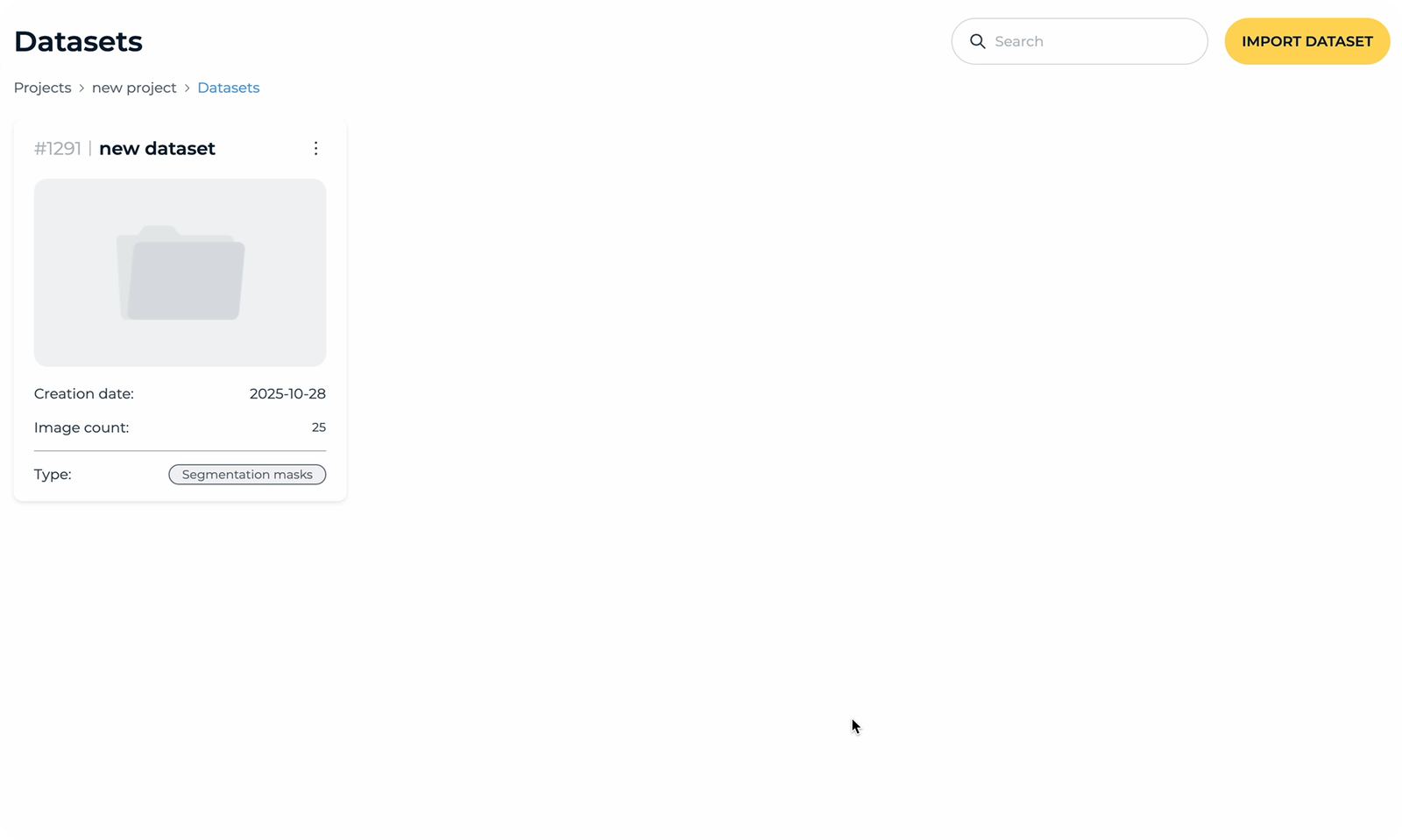
 Datasets
Datasets

The user begins by setting up a new project, specifying a name and choosing the dataset source. This step initializes the workspace and prepares the platform to handle image data for further processing.
Import Dataset
Users import images by connecting to existing storage, such as AWS S3 buckets, so the platform can analyze the dataset and extract key information like the number of images, classes, and metadata.

How to Add Classes
The user selects an image from the imported dataset and opens the Annotation Tool. They use polygons to mark the areas of defects.
Users assign a name to the new class and use polygons to mark the relevant areas of the defect on the image. Multiple polygons can be combined to accurately highlight complex defects or objects of interest.
Once the class is defined and labeled, the annotation is saved, which is then applied to the dataset, making it ready for generating synthetic images.
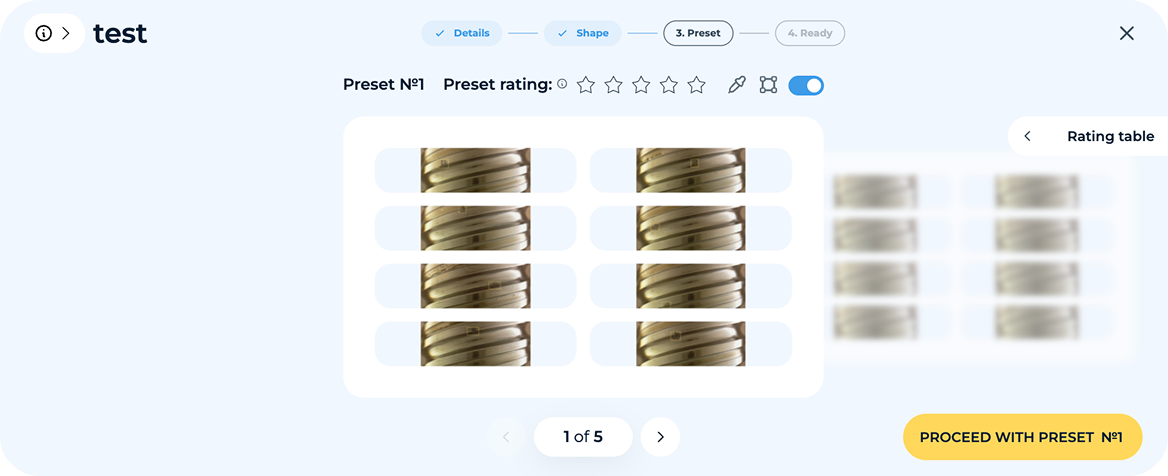
Concept Creation
Choose a subset of images from the imported dataset and provide a prompt or description of the defect to model.
Exclude images with poor annotations or irrelevant defects to maintain data quality.
Set the concept’s shape settings—select polygons, circles, or rectangles, and adjust size and variation.
After creating the concept, generate preview images to review and provide feedback.

AI Refinement Loop
After the first set of synthetic images is generated, users review a sample and provide feedback on quality, accuracy, and realism. The platform automatically processes this feedback, adjusting shapes, variations, and defect placement to improve future generations. This iterative process continues until the user is satisfied.
Generate Batch
Once the concept has gone through refinement and the user is satisfied with the results, they can generate a full batch of synthetic images. The batch can include hundreds or even thousands of images, all based on the approved concept and defect variations.
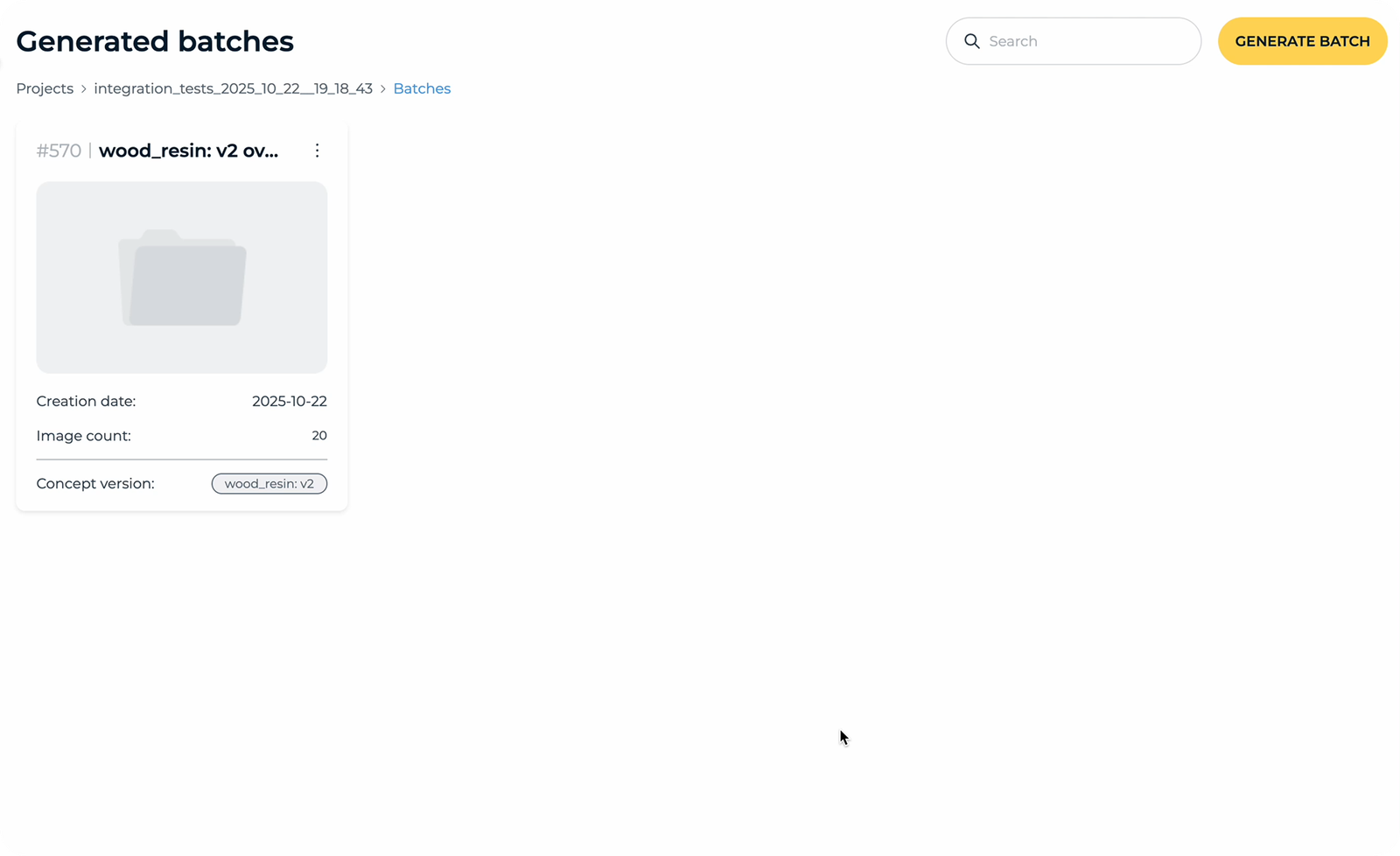
Users can train ML models using datasets and batches prepared in previous steps. Both labeled and unlabeled images, along with synthetic batches, can be used as input data.
How to Train the Model?

Users choose datasets and/or synthetic batches to feed into the model.
Users select batches, choose specific images for training, define classes, pick a dataset, set up validation etc.
Once all parameters are set, the model is ready for training. After clicking the start button, the process begins.
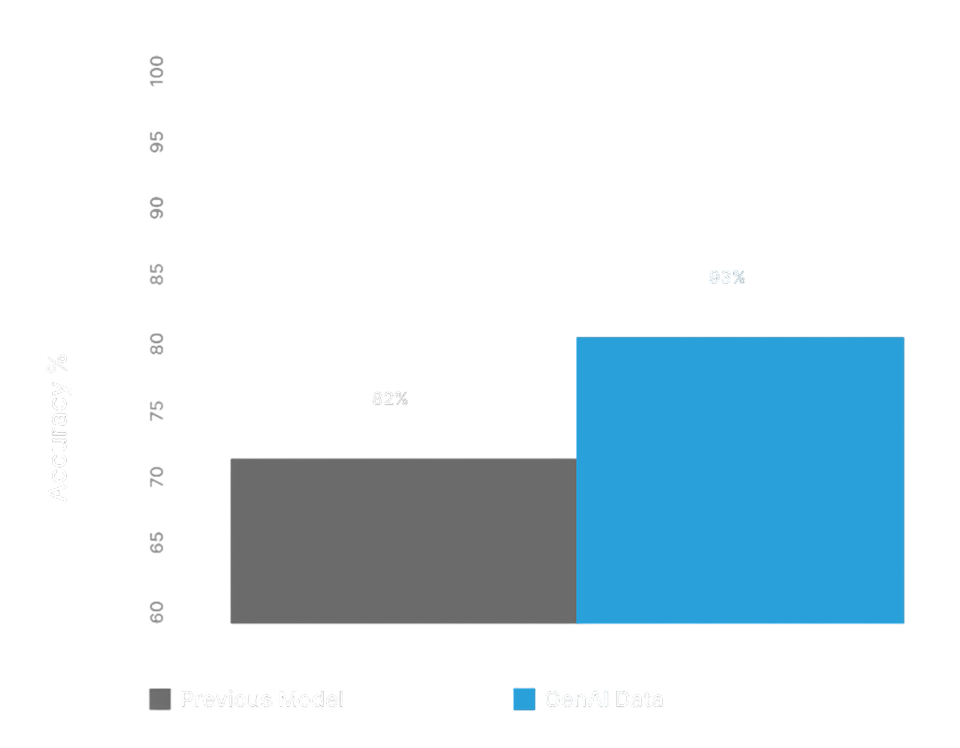
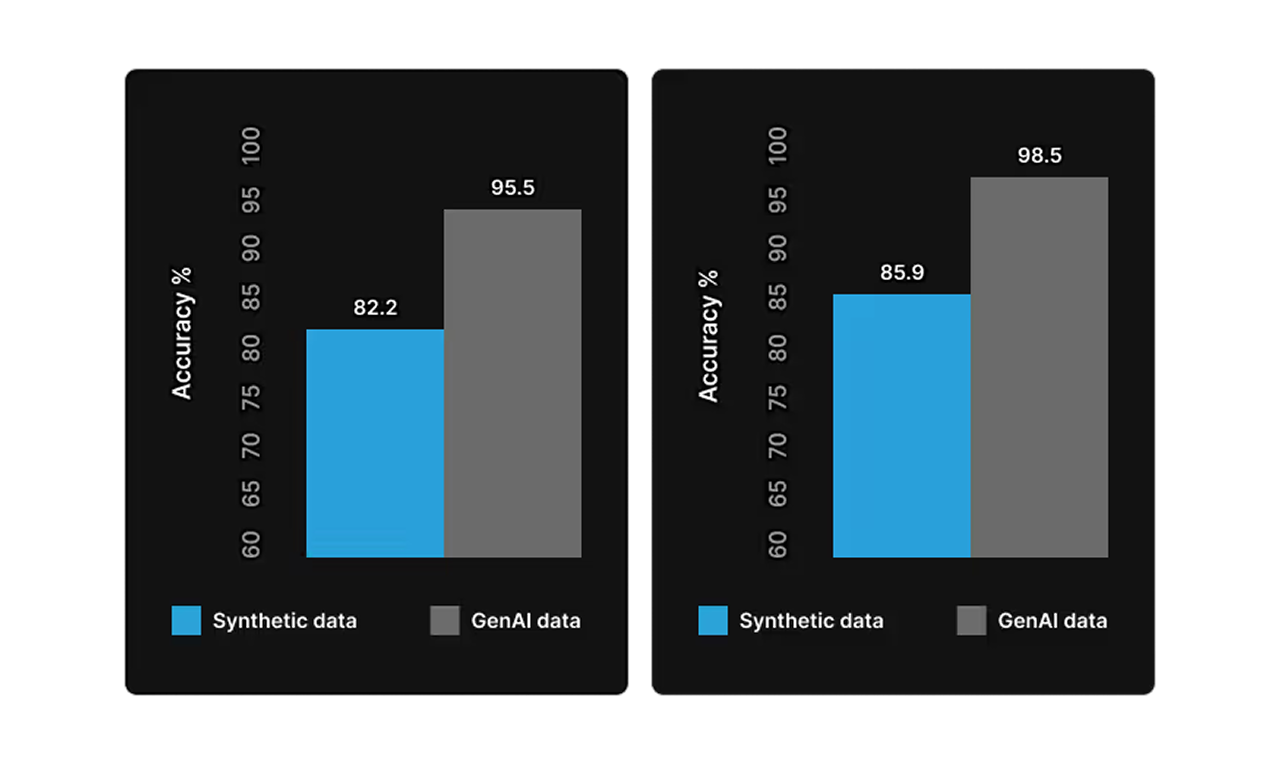
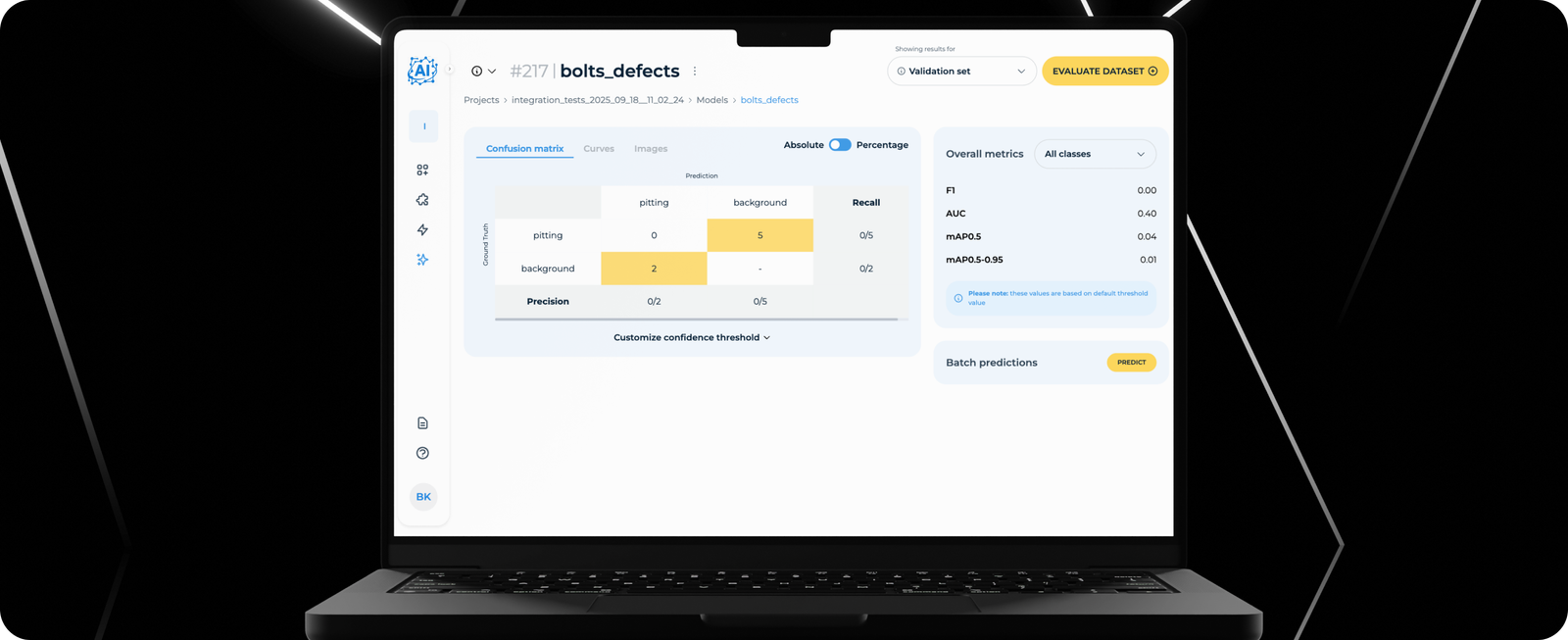
Once training is complete, users can review metrics and assess how well the model performs on defect detection.
Final Results
Thanks to the intuitive workflow and the convenient Annotation Tool, users can easily label defects, making dataset preparation fast, precise, and effortless, even for complex images.

We leveraged AWS Lambda for serverless processing and SageMaker for AI model deployment. This setup provided scalable, efficient, and low-maintenance infrastructure for training models and generating synthetic images.
We implemented a fully serverless AWS architecture, automating scaling, monitoring, and secure data handling. This ensured reliable performance with large datasets and high-volume batch generation.